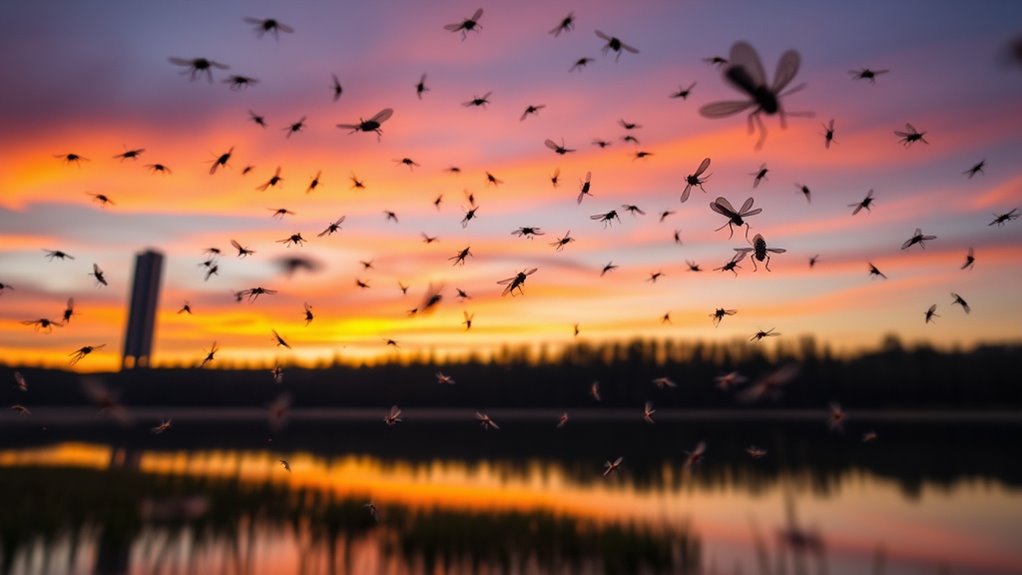
Mosquitoes typically fly at altitudes of 1 to 10 feet, which is about one to two floors in height. Their lightweight exoskeleton and specialized wing structure enable agility and rapid flapping for lift, allowing for effective host location. Factors like temperature, humidity, and wind impact flight patterns and stability. Understanding these dynamics is essential, especially for pest control measures. There's more to discover about how these factors influence mosquito behavior and your interactions with them.
The Anatomy of a Mosquito: Flight Adaptations

While you might think of mosquitoes as mere nuisances, their anatomy reveals a complex set of adaptations that enable efficient flight. The mosquito's lightweight exoskeleton minimizes drag, while its long, slender wings are perfectly shaped for agility. Each wing's unique structure allows for rapid flapping, which enhances lift and maneuverability. The flight mechanics are further optimized by a specialized set of muscles that control wingbeat frequency, enabling quick responses to environmental changes. Additionally, the halteres—small balancing organs—assist in stabilizing flight, allowing for precise navigation. These anatomical features collectively enhance a mosquito's ability to fly effectively, showcasing an intricate design tailored for survival. Understanding these adaptations can deepen your appreciation for the resilience and efficiency of these insects.
Factors Influencing Mosquito Flight Height
Factors influencing mosquito flight height are multifaceted, incorporating environmental, physiological, and behavioral elements. Understanding these can give you insight into mosquito behavior and flight patterns.
- Temperature: Warmer conditions can enhance metabolic rates, allowing mosquitoes to fly higher.
- Humidity: Increased moisture levels often lead to more buoyant air, affecting how high mosquitoes can ascend.
- Wind: Strong winds can disrupt flight patterns, forcing mosquitoes to stay lower or seek shelter.
- Availability of Hosts: The presence of hosts can dictate flight height, as mosquitoes often adjust their altitude to find suitable feeding opportunities.
Typical Altitude Ranges for Mosquitoes

Mosquitoes typically fly at altitudes ranging from a few inches to several feet above the ground, with most activity concentrated between 1 to 10 feet. This altitude range is essential for understanding mosquito behavior and their flight patterns. At these heights, mosquitoes effectively locate hosts and evade obstacles like vegetation. Their flight patterns exhibit a tendency to hover and dart, enabling them to navigate through their environment efficiently. This behavior is not random; instead, it's a strategic adaptation to optimize survival and reproduction. By maintaining this altitude, mosquitoes can exploit favorable conditions, such as wind currents, while minimizing exposure to predators. Understanding these typical altitude ranges provides insight into their ecological role and interactions within diverse habitats.
How Weather Conditions Affect Mosquito Flight
Altitude ranges are just one aspect of how environmental conditions influence mosquito behavior. Weather plays an important role in determining how high and far these insects can fly. Here are four key factors to take into account:
- Temperature: Warmer temperatures increase metabolic rates, enhancing flight activity.
- Humidity: High humidity levels support longer flights, as mosquitoes lose less water.
- Wind: Strong winds can hinder flight, pushing mosquitoes to lower altitudes for stability.
- Precipitation: Rain can disrupt their flight patterns, as wet conditions lead to increased ground-level activity.
Understanding these environmental impacts can help predict mosquito behavior and their potential range, allowing for better management strategies in various settings.
Implications of Mosquito Flight Heights for Human Interaction

While many may not realize it, the height at which mosquitoes fly can notably impact human interactions and public health. In urban environments, mosquitoes often navigate through various vertical layers, influencing human behavior considerably. When they fly at lower altitudes, they're more likely to encounter individuals, increasing the probability of bites and potential disease transmission. Additionally, as urban areas expand vertically with high-rise buildings, understanding their flight patterns becomes essential for effective pest control strategies. This knowledge can help you implement preventative measures, such as installing screens or using repellents more effectively. Ultimately, recognizing the implications of mosquito flight heights can empower you to take informed actions that enhance your well-being and overall quality of life in densely populated areas.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Can Mosquitoes Sustain Flight Without Resting?
Have you ever wondered just how long those pesky mosquitoes can stay airborne? Their flight duration is surprisingly limited; they typically sustain flight for about 30 minutes to an hour. This time frame is primarily dictated by their energy consumption. As they navigate through the air, they rapidly expend energy, necessitating rest. So, while they might seem like relentless pests, they're bound by their own biological constraints, just like us.
Do Different Mosquito Species Have Varying Flight Capabilities?
Yes, different mosquito species do exhibit species differences in flight capabilities. Some can reach impressive flight altitudes, while others prefer lower elevations. Factors like size, wing structure, and environmental conditions influence these variations. For instance, Aedes mosquitoes are known for their ability to fly at higher altitudes compared to Culex species, which often remain closer to the ground. Understanding these differences can help you manage mosquito populations more effectively in your area.
Can Mosquitoes Fly Indoors as High as Outdoors?
Imagine a bird in a cage, its wings clipped yet still yearning for the sky. Similarly, mosquitoes can fly indoors but face altitude limitations compared to their outdoor escapades. Indoor flight often occurs at lower heights due to structural constraints and airflow patterns, which can hinder their ability to soar. While they can navigate rooms, their flight height is generally restricted, making their indoor experience quite different from the freedom of the open air.
What Role Do Predators Play in Mosquito Flight Patterns?
Predators greatly impact mosquito flight behavior. When you consider the presence of predators, mosquitoes adjust their movements to avoid detection. This avoidance strategy can alter their flight patterns, making them fly lower or change direction more frequently. By understanding predator impact, you can appreciate how these dynamics shape mosquito populations and their survival tactics. Fundamentally, the threat of predation forces mosquitoes to be more cautious and adaptive in their flight behavior.
How Do Mosquitoes Navigate While Flying?
When you consider how mosquitoes navigate while flying, you'll find that their vision and sensory cues play essential roles. Mosquitoes possess compound eyes that detect movement and light, allowing them to orient themselves effectively. They also rely on sensory cues, like carbon dioxide and heat from potential hosts, to guide their flight paths. This combination of visual and sensory information enables mosquitoes to navigate through complex environments with remarkable precision.